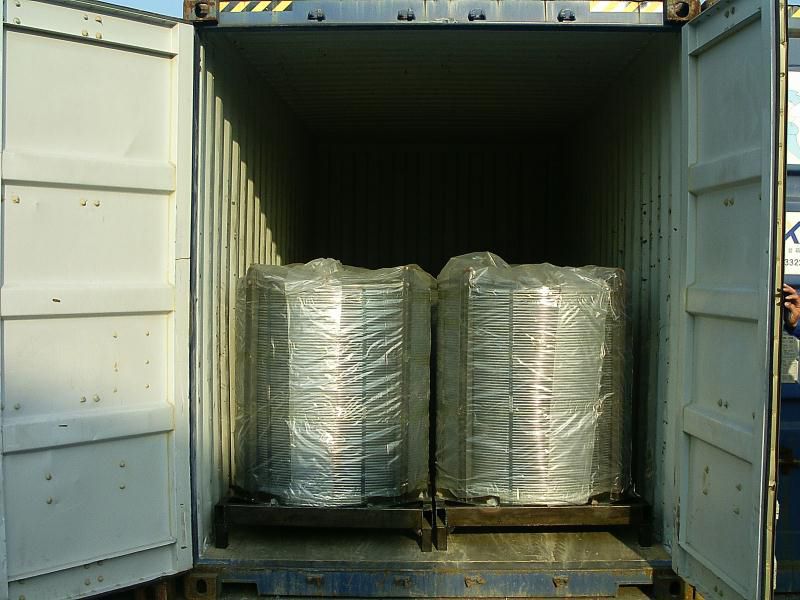
Products
Specification
| Grade | SIC(≥) | Free Carbon | Fe2O3 |
| SIC98.5 | 98.5 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| SIC97 | 97 | 0.3 | 1.2 |
| SIC95 | 95 | 0.6 | 1.2 |
| SIC90 | 90 | 1 | 1.2 |
| SIC88 | 88 | 4 | 1.5 |
| SIC85 | 85 | 5 | 3 |
| SIC80 | 80 | 5 | 3 |
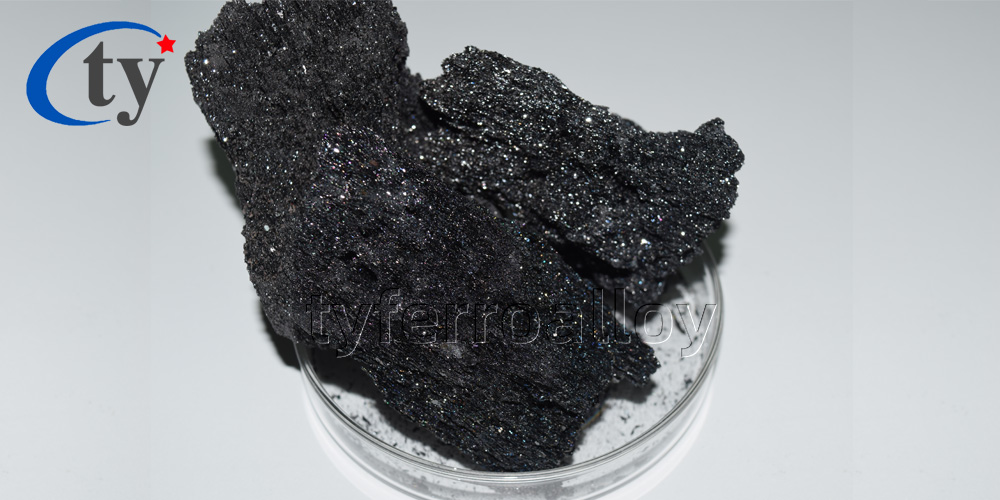
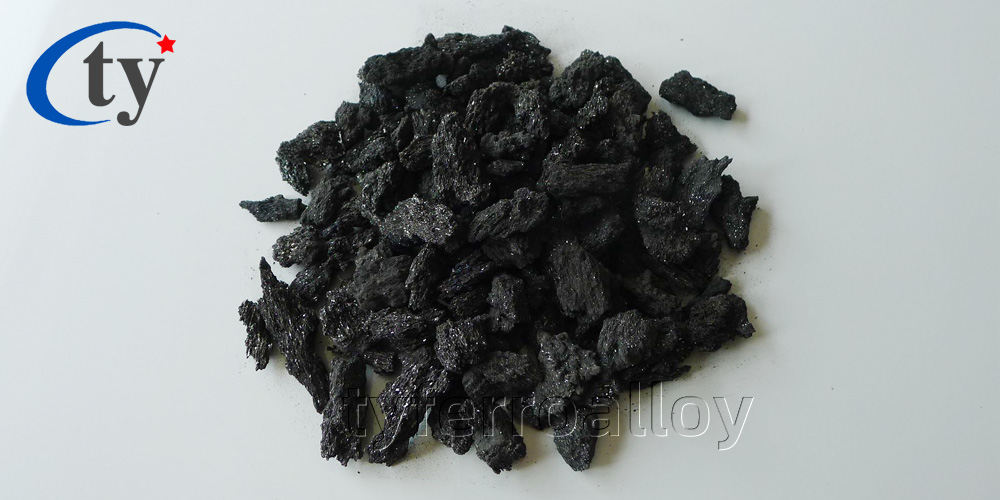
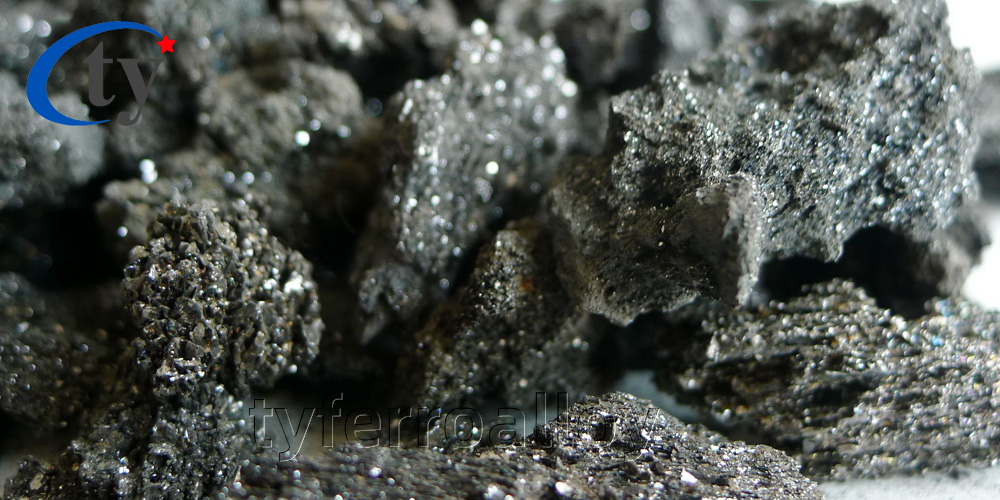
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is a man-made material manufactured through heating silica sand and carbon to high temperatures in the Acheson furnace technique. Silicon carbide is an extremely hard material (Mohs hardness 9.25), is chemically inert and does not melt. Silicon Carbide has a high thermal conductivity, a low coefficient of thermal expansion, is thermal shock and abrasion resistant and has strength at high temperatures. Silicon carbide's varied properties make it an effective material in many different applications.
Silicon carbide contains two common basic varieties: black silicon carbide and green silicon carbide. Black silicon carbide contains sic about 95%, so the toughness is higher than green silicon carbide. It is widely used for processing low tensile strength material like glass, ceramics, stone, refractory material, cast iron and nonferrous metal etc. Green silicon carbide contains sic about 97% above with good self-sharpening, so it is used for processing hard alloy, titanium alloy and optical glass as well as cylinder jacket and fine grinding cutting tools.
Silicon carbide has good hardness only second to the hardest diamond, hardness is 9.5. Due to good thermal conductivity, silicon carbide is a kind of semiconductor and can oxidation resistance in high temperature. Silicon carbide has wide applications because of stable chemical performance, high thermal conductivity, small thermal expansion coefficient, good wear-resisting performance. Low grade silicon carbide about 85% is an excellent deoxidizer, which can speed up steel making and facilitate the control of chemical composition to improve the steel quality. Therefore, the market price of silicon carbide is still stable.